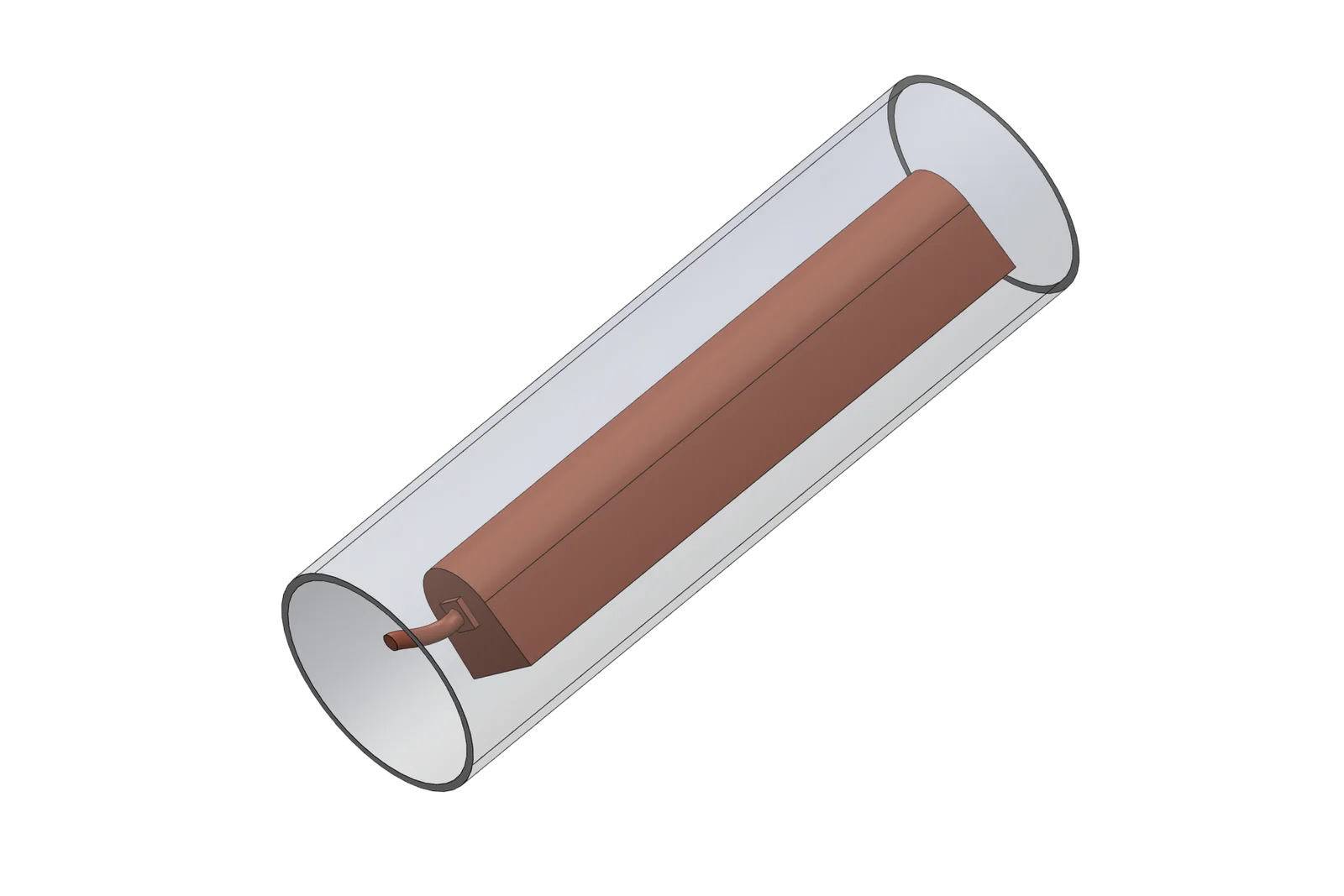
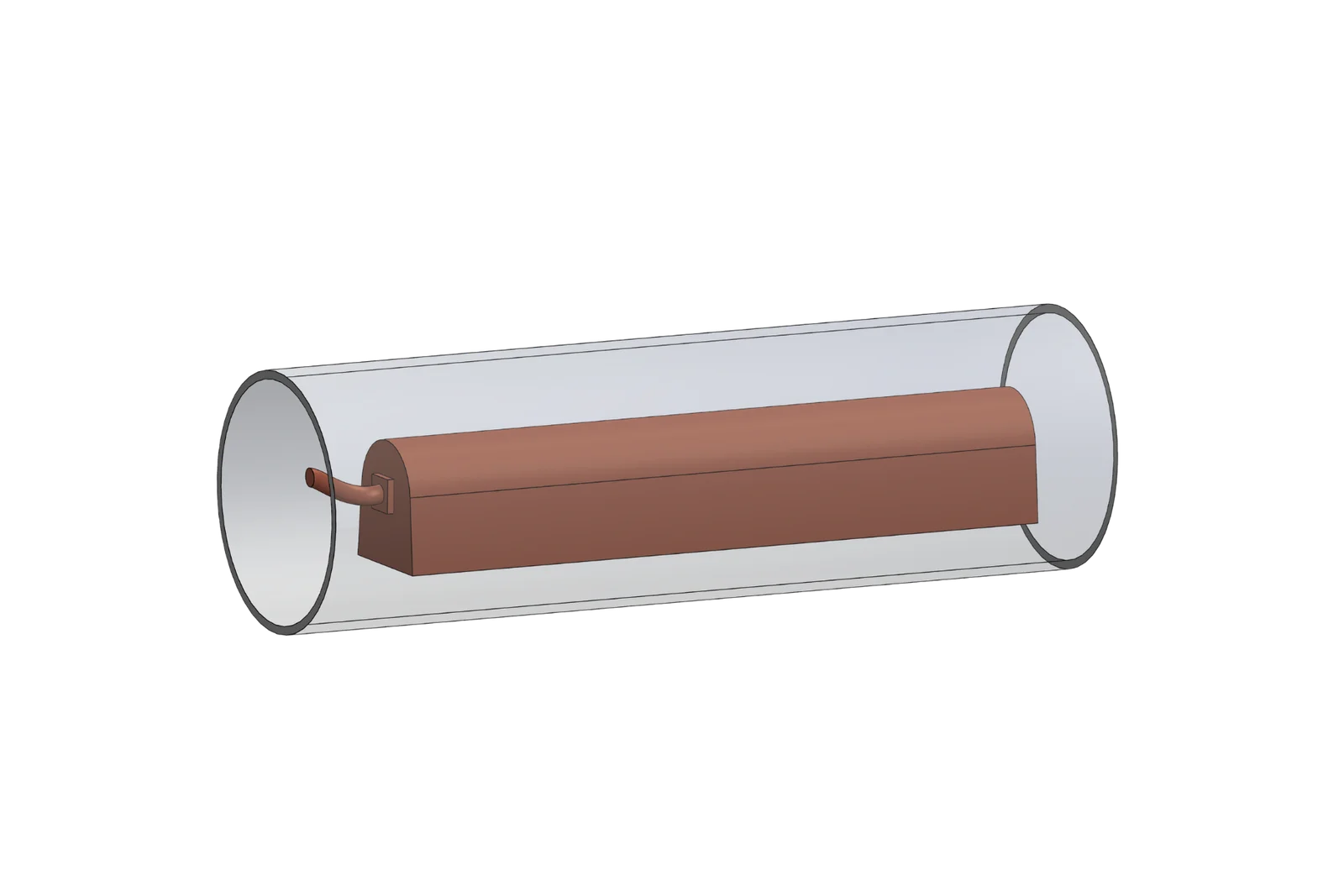
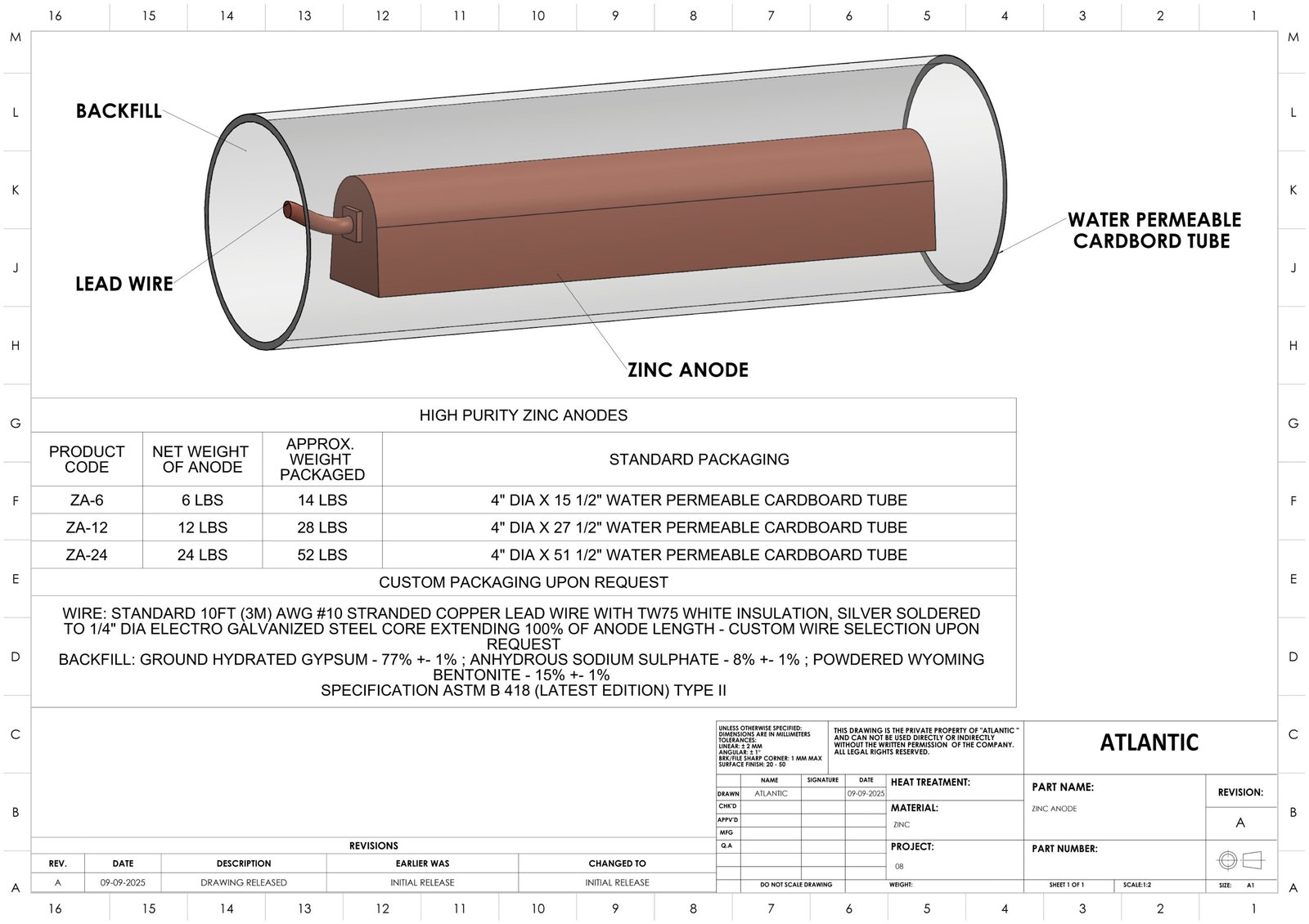
Zinc Anodes are designed to provide highly effective sacrificial corrosion protection for steel structures in cathodic protection systems. With stable electro chemical performance and controlled driving potential, they ensure long-term protection in soil, freshwater, and other low-resistivity environments.
| Item |
Zinc Anodes |
| Product Description |
High Purity Zinc Anodes |
| Material |
Zinc |
| Coating |
Uncoated |
| Standard / Classifications |
ASTM G97-97 |
Installation Steps
- Select the appropriate zinc anode size and type based on the specific marine or underground application.
- Clean the metal surface of the structure to ensure proper electrical connection.
- Position the zinc anode in direct contact with water or soil where corrosion protection is required.
- Attach the anode securely using approved clamps, welds, or bolted connections depending on the application.
- Ensure the anode has a solid electrical connection to the structure by checking continuity with a meter.
- For underground use, place the anode in a moist, conductive environment to maximize performance.
- Verify proper installation by measuring the protection potential after the anode is fixed in place.
Common Applications
- Where the sulphur present in the water.
- where there is hard water or little intrusion of salt water
- There is need of slow corroding anode in aggressive water condition.
- Marine Vessels: Used to protect ship hulls, rudders, and propellers from galvanic corrosion in
seawater
- Offshore Structures: Ideal for platforms, piers, and submerged components exposed to saltwater
- Underground Pipelines: Provides cathodic protection in high-conductivity soils
- Storage Tanks: Protects the internal and external surfaces of steel tanks in marine or coastal
environments
- Heat Exchangers & Condensers: Prevents corrosion in cooling water systems and marine HVAC
units